What Is Adolescent Medicine? Roles, Services, and Trends
Key Takeaways
- Adolescent medicine helps teens navigate the important shift from childhood to adulthood by focusing on their physical, emotional, and social well-being.
- Doctors in this field handle health check-ups, mental health problems, and substance use prevention, often working with other specialists.
- Doctors who want to specialize in adolescent medicine, besides medical school, must complete additional training, a residency, and a specialized program focused on teen health.
- New tools like telemedicine and health apps are changing the way teens get care, making it easier and more flexible to get the help they need.
The medical needs of adolescents and young adults are the focus of the specialized field of adolescent medicine – a time of significant physical, emotional, and social change. This transitional stage between childhood and adulthood presents unique challenges.
One in seven children between the ages of 10 and 19 worldwide has a mental illness. This highlights the urgent need for targeted adolescent treatment. Adolescent medicine plays a vital role in treating both physical and psychological health concerns, and teens need care that is tailored to their individual requirements during this critical period.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!
YOUR PATH TO SUCCESS BEGINS HERE
What Is Adolescent Medicine?
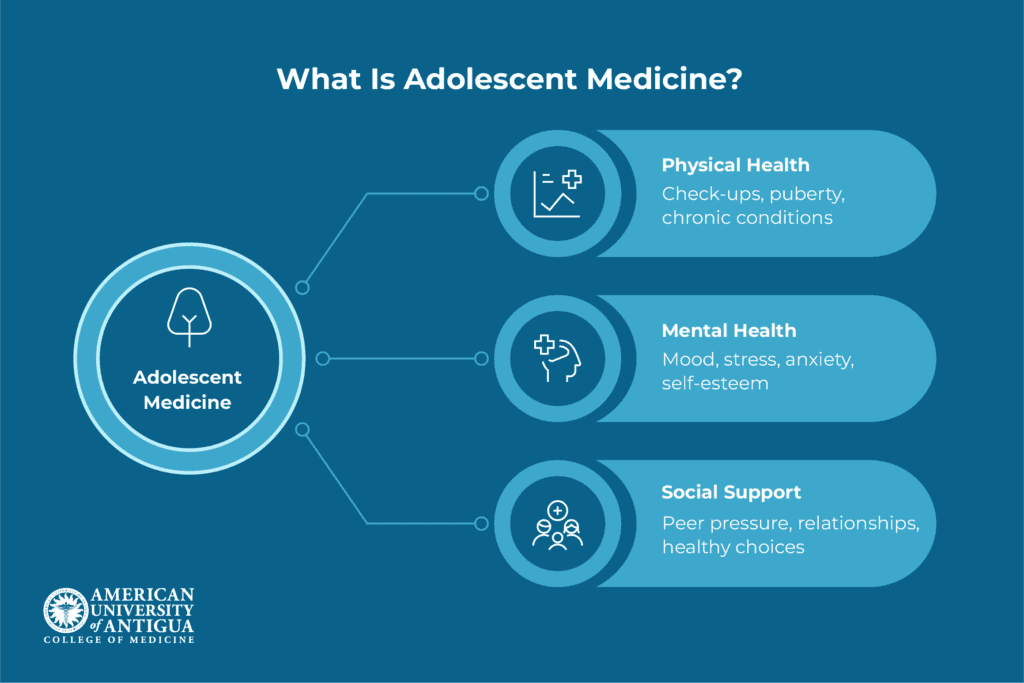
Adolescent medicine is a type of healthcare that focuses on the needs of young people between the ages of 10 and 19. It’s different from regular pediatrics, which treats younger children, and adult medicine, which deals with fully grown adults. This area of medicine helps teens through the many changes they go through – like puberty, mental health struggles, and social pressures.
Doctors in adolescent medicine take a holistic approach, addressing not just physical health but also emotional well-being, healthy habits, relationships, and any medical issues teens might face, ensuring they’re supported as they grow into adults.
Who Are Adolescent Medicine Specialists?
Adolescent medicine specialists are doctors who focus on the unique health needs of teenagers and young adults. After completing medical school and training in general pediatrics, internal medicine, or family medicine, they receive additional training in adolescent health.
These specialists often team up with pediatricians, psychologists, social workers, and other healthcare providers to care for all parts of a teen’s health. They’re also great at earning their trust and talking with them and their families in a way that helps everyone feel comfortable sharing personal or sensitive concerns.
Their goal is to guide adolescents through this important stage of life with care that addresses both physical and emotional health.
Key Aspects of Care in Adolescent Medicine

Adolescent medicine covers a wide range of services designed to support teens during a time of major physical and emotional changes. Teens often go through challenges like mood changes, peer pressure, hormonal shifts, and difficulties with relationships and self-identity.
To help with these concerns, adolescent medicine specialists provide care in important areas such as physical and mental health, reproductive health, and substance use screening and counseling. In the following sections, we’ll explore each of these key aspects in detail.
Physical health services
Adolescent medicine provides regular check-ups to ensure teens are growing and developing in a healthy way. These visits typically include:
- Checking height, weight, and blood pressure
- Reviewing eating habits and physical activity levels
- Making sure all vaccinations are current
During these visits, doctors also assess for common health concerns such as:
- Acne
- Sports-related injuries
- Menstrual or period-related issues
- Chronic conditions like asthma or diabetes
These check-ups are usually led by pediatricians or adolescent medicine specialists, who help teens manage the physical changes that occur during puberty and stay on a healthy path.
Mental health support
Mental health is a big part of adolescent care since many teens deal with stress, anxiety, or changes in mood. During a check-up, doctors may ask about how the teen is feeling, sleeping, doing in school, and getting along with others. This helps them find out if there are any emotional or mental health concerns like depression, low self-esteem, or eating problems.
Support in this area often comes from a team that may include adolescent doctors, psychologists, counselors, or psychiatrists, who work together to help teens feel better and stay mentally strong.
Sexual and reproductive health
As teens go through puberty, they may have questions or concerns about their bodies and changes in their reproductive system. Adolescent medicine offers private and respectful care in this area, which can include help with menstrual health, guidance on hygiene, and testing for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) if needed.
These visits provide a chance for teens to learn more about their bodies in a safe and supportive setting. Care in this area may be provided by adolescent medicine specialists, OB/GYNs, or nurse practitioners who are experienced in working with teens.
Substance use screening and counseling
Adolescent medicine also focuses on helping teens avoid or deal with substance use, such as smoking, drinking, or drug use. During a visit, doctors may ask questions in a calm and supportive way to find out if the teen is using anything harmful or feeling pressure to try it. If they are, the doctor can offer guidance, support, and ways to stop or avoid risky behavior.
In more serious cases, they may bring in counselors, therapists, or addiction specialists to help. These services are usually led by adolescent medicine providers with help from mental health experts.
How to Become an Adolescent Medicine Specialist

Becoming an adolescent medicine specialist requires a focused educational and clinical path designed around the unique health needs of teenagers and young adults. Here’s how to get there:
- Earn a medical degree (MD or DO) by completing medical school.
- Complete a residency in one of the following:
- Internal medicine
- Family medicine
- Pediatrics
- Pursue a fellowship in adolescent medicine, which typically lasts 1–2 years and provides specialized training in managing:
- Physical health concerns
- Emotional challenges
- Mental health conditions during adolescence
- Obtain board certification by passing exams from the American Board of Pediatrics or other relevant medical boards.
At AUAMED, students interested in adolescent medicine can access comprehensive programs that prepare them with the clinical knowledge and hands-on experience required for this specialty.
In addition to medical training, successful adolescent medicine specialists must develop these skills:
- Strong communication
- Empathy
- Cultural competency
These qualities are essential for building trust and effectively supporting the diverse needs of teens and their families.
Emerging Trends in Adolescent Medicine

Adolescent medicine is evolving rapidly, with modern tools and approaches making it easier to care for teens and young adults. Telemedicine has become an important part of this change, allowing doctors to offer care remotely and improving access for many adolescents.
Digital tools like mobile apps and online platforms are also helping teens manage mental health issues such as anxiety and depression. By combining mental health care with routine check-ups, providers can offer more complete care that supports both the body and mind.
In addition, public health initiatives and new policies are helping shape the future of adolescent healthcare. More digital programs now offer mental health support, giving teens more options to get the help they need. Policy changes that improve healthcare protections also aim to make care more fair and accessible for everyone.
At the same time, new policies, like better healthcare protections for LGBTQ+ individuals, aim to reduce unfair treatment and ensure equal care. These trends show how adolescent medicine is always adapting to better meet the needs of teens, making healthcare more inclusive and accessible.
Conclusion
Adolescent medicine is essential because it addresses the unique healthcare needs of teenagers and young adults during a critical stage of their development. With specialized care, healthcare providers can support both physical and mental health, helping adolescents navigate the challenges of puberty, emotional changes, and social pressures.
By offering tailored services that focus on the whole person, adolescent medicine ensures that teens receive comprehensive care that prepares them for a healthy adulthood. Specialized care during this time fosters better health outcomes and equips teens with the tools they need to thrive.
If you’re interested in learning more about adolescent medicine, explore AUAMED’s program offerings, with courses that have a a strong foundation for those looking to specialize in this important healthcare field.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What does “adolescent patients” mean?
Adolescent patients are individuals, typically ages 10 to 19 years, who are going through the developmental stages of puberty and adolescence.
What is the scope of adolescent medicine?
Adolescent medicine focuses on the physical, emotional, and social health of teens, addressing issues like growth, mental health, sexual health, and substance use.
Is adolescent medicine and pediatric medicine the same?
Adolescent medicine is a subspecialty within pediatrics, focusing specifically on the unique healthcare needs of teenagers, whereas pediatric medicine covers a broader range of care for children from infancy to adolescence.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!
YOUR PATH TO SUCCESS BEGINS HERE
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!