What Is a Gynecologist and Why You Should See One
Gynecologists are the guardians of women’s health, specializing in the care and management of the female reproductive system. From adolescence through menopause and beyond, these dedicated professionals provide essential services that support women at every stage of life.
Whether it’s guiding young women through their first reproductive health questions, assisting with family planning and pregnancy, or addressing the complexities of menopause, gynecologists play a vital role in maintaining overall well-being.
This blog post will delve into the world of gynecologists, exploring what they are, their importance in medicine, the various reasons women seek their expertise, and what to expect during a visit.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!
YOUR PATH TO SUCCESS BEGINS HERE
What Is a Gynecologist?
A gynecologist is a doctor who specializes in women’s reproductive health. They focus on the female reproductive system, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and breasts. As such, they handle a wide range of issues, from menstruation and fertility to sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and hormone disorders. They also conduct routine exams to detect any conditions that need medical attention.
Gynecologists also specialize in providing care during pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause. Their goal is to help women maintain their reproductive health through various stages of life, ensuring any problems are detected and treated early.
What Does a Gynecologist Do?
A gynecologist’s daily tasks include examining patients, diagnosing conditions, and providing treatment. They perform various types of exams, such as:
- Pelvic exams to check the reproductive organs
- Pap smears to screen for cervical cancer
- Breast exams to detect lumps or other issues
Gynecologists also conduct procedures like:
- Hysterectomies (removal of the uterus)
- Laparoscopies (minimally invasive surgeries)
- Biopsies (taking tissue samples for testing)
In addition to exams and procedures, gynecologists give advice on contraception, helping women choose the best birth control method for them. They also help manage symptoms of menopause, like hot flashes and mood changes, ensuring women remain healthy and comfortable.
What Conditions Do Gynecologists Treat?
Gynecologists treat various conditions related to women’s reproductive health, including:
- Menstrual disorders: Problems with the menstrual cycle
- Endometriosis: Tissue similar to the uterus lining grows outside the uterus
- Fibroids: Non-cancerous growths in the uterus
- Ovarian cysts: Fluid-filled sacs in the ovaries
They also manage sexually transmitted infections (STIs), like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and HPV, providing treatment to clear these infections and prevent complications.
Reproductive health is another area of focus, where gynecologists offer treatments to help women conceive, and pregnancy-related care, monitoring the health of both mother and baby throughout pregnancy and childbirth.
Cancer screenings are also a vital part of their job. They perform Pap smears to detect cervical cancer and other tests to check for cancers of the reproductive organs, including the uterus and ovaries. If cancer is detected, they provide treatments and refer patients to specialists, ensuring comprehensive care.
How to Become a Gynecologist?
To become a gynecologist, one must follow an educational and training path that begins with undergraduate studies in a related field, continues to medical school, and ultimately leads to certification.
Educational Requirements
First, you must earn a bachelor’s degree, usually in a science-related field. After completing your undergraduate studies, you need to attend medical school, which typically takes four years. In medical school, you study a broad range of medical topics and gain hands-on experience through clinical rotations.
Residency Program
After medical school, you must complete a residency program in obstetrics and gynecology. This residency usually lasts four years and involves intensive training in both obstetrics (pregnancy and childbirth) and gynecology (women’s reproductive health). During this time, you gain practical experience by working with patients under the supervision of experienced doctors.
Licensing and Certification
Once you finish your residency, you need to obtain a medical license to practice. This involves passing a series of exams. Additionally, many gynecologists choose to become board-certified by passing a rigorous exam from the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ABOG). Board certification demonstrates a higher level of expertise and commitment to the field.
Subspecialties
Within gynecology, there are several subspecialties you can pursue with additional training. These include reproductive endocrinology, which focuses on fertility issues, and gynecologic oncology, which involves the treatment of cancers related to the female reproductive system. Other subspecialties include maternal-fetal medicine and urogynecology, each requiring additional fellowship training after residency.
When Should You Start Seeing a Gynecologist?
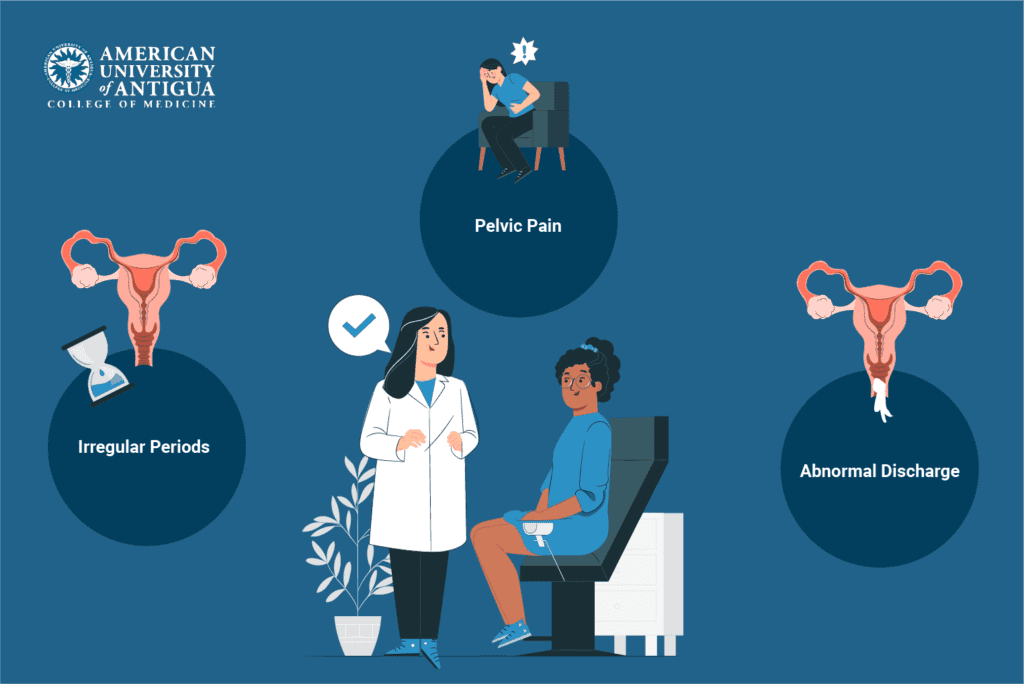
It is recommended that you start seeing a gynecologist in your teens, typically between ages 13 and 15, or when you become sexually active. Routine check-ups with a gynecologist should happen once a year. These annual visits help monitor your reproductive health and detect any potential issues early.
There are certain signs and symptoms that should prompt a visit to the gynecologist, even if it’s not time for your routine check-up. These include:
- Irregular Periods: If your menstrual cycle is unpredictable, very heavy, or if you miss periods without being pregnant.
- Pelvic Pain: Persistent or severe pain in your lower abdomen or pelvic area.
- Abnormal Discharge: Unusual discharge from the vagina, especially if it has a strong odor, changes color, or is accompanied by itching or irritation.
Visiting a gynecologist when these issues arise helps ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
What to Expect During an Appointment With a Gynecologist
A standard gynecological appointment typically begins with a discussion of your medical history. This is important because it helps the gynecologist understand your overall health and any specific concerns you might have. After the discussion, a physical examination is performed, which often includes a breast exam to check for lumps and a pelvic exam to inspect the reproductive organs.
Common procedures during the visit may include a Pap smear, which involves collecting cells from the cervix to screen for cervical cancer, and a pelvic exam to check the health of your uterus, ovaries, and other reproductive organs.
To prepare for your appointment, start with an open mind; being open and honest with your gynecologist is key to getting the best care. Think about writing down any symptoms or questions you have.
For example, it’s helpful to ask your gynecologist about birth control options, any changes in your menstrual cycle, or concerns about pain or discharge. Wearing comfortable clothing and ensuring personal hygiene can also make the appointment smoother.
Remember that a regular check-up with your gynecologist can make all the difference.
Salary of a Gynecologist
The salary of a gynecologist depends heavily on a variety of factors. Location, experience, and workplace all play a significant role on the average annual income for gynecologists. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, these healthcare professionals accumulate $278,660 per year, on average.
However, gynecologists in large cities or high-demand areas often earn more than those in rural locations; more experienced gynecologists also tend to have higher salaries. Gynecologists working in private practice or specialized fields, such as reproductive endocrinology or gynecologic oncology, may earn even higher incomes.
In addition to salary, gynecologists often enjoy other benefits and perks, including job security, as there is always a need for their expertise.
They also have flexibility in their schedules, especially those in private practice who can set their own hours. This combination of good salary, job security, and flexibility makes gynecology an attractive career choice for many.
Conclusion
Gynecologists have a significant impact on maintaining women’s health, offering vital treatment and support. These are experts who, after going through a rigid educational and training path, specialize in areas like the reproductive system, menstrual cycle, and more. Regular visits to a gynecologist are important for preventive care, catching potential problems early, and maintaining overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What’s the difference between a gynecologist and an OBGYN?
A gynecologist specializes in women’s reproductive health, while an OBGYN is trained in both gynecology and obstetrics, which includes pregnancy and childbirth care.
How often should I visit a gynecologist?
You should visit a gynecologist once a year for routine check-ups. Additional visits are recommended if you experience symptoms like irregular periods, pelvic pain, or abnormal discharge.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!