What Is Telemedicine? Definition, Benefits & How It Works
Key Takeaways
- Telemedicine makes healthcare more accessible, convenient, and cost-effective for patients and providers.
- It uses technologies like video calls, mobile apps, and remote monitoring to deliver care outside traditional clinics.
- The future of telemedicine includes AI, smart wearables, and even remote surgeries, offering exciting opportunities in digital health.
Telemedicine is no longer just a buzzword. It’s quickly becoming a go-to option for healthcare. Thanks to the rise of digital health solutions, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, more people are turning to remote care for convenience and speed.
Whether it’s a quick video call with your doctor or managing chronic conditions from home, telemedicine is changing how we think about healthcare. It’s gaining traction among patients, providers, and even policy makers because it saves time, reduces costs, and makes care more accessible.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!
So, what is telemedicine exactly? Let’s break it down and see how it all works.
What Is Telemedicine?
Telemedicine is the use of digital technology to deliver clinical healthcare services remotely. It includes real-time consultations, diagnoses, and follow-up care using secure video calls, phone, or messaging platforms. Unlike wellness apps or health trackers, telemedicine focuses on direct interaction between patients and licensed healthcare providers.
According to the World Health Organization, it’s a way to improve access to medical care, especially in areas with limited healthcare resources. Whether you’re consulting with a doctor about symptoms or managing a chronic condition, telemedicine brings clinical care to your screen – safely, efficiently, and without the waiting room.
How Does Telemedicine Work?
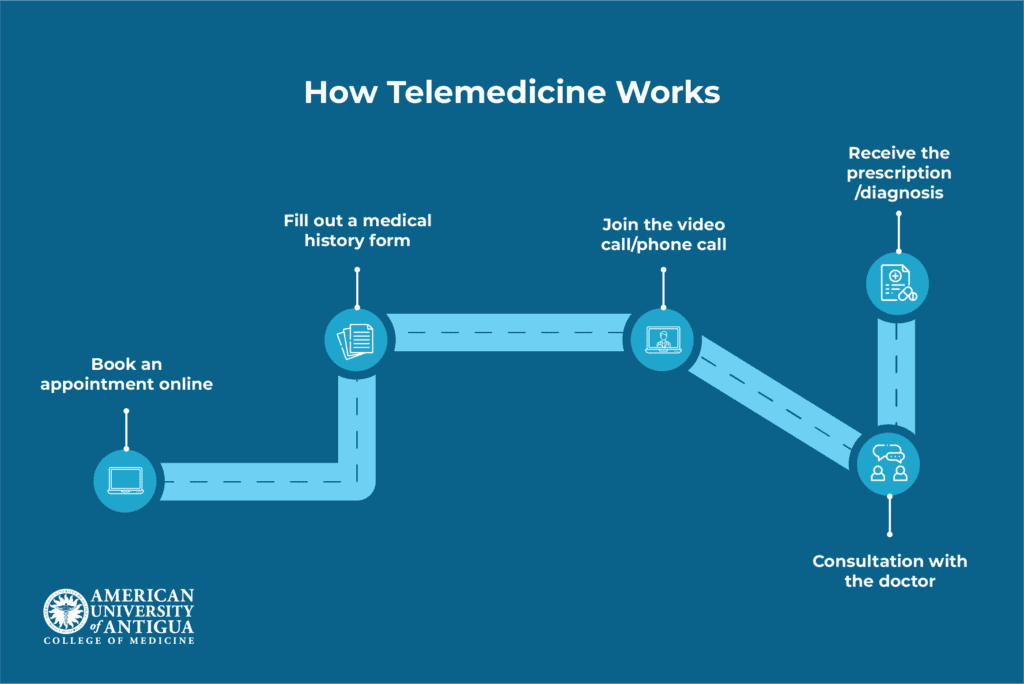
Telemedicine works by connecting patients and healthcare providers through secure digital platforms. Using smartphones, tablets, or computers, people can schedule appointments, share health data, and speak with doctors in real-time. Behind the scenes, reliable internet, video software, and electronic health records make the whole process smooth and efficient.
The patient journey
You start by booking an appointment through your healthcare provider’s app, website, or online portal. It only takes a few clicks to choose a time that works for you. Before the session, you might be asked to fill out a quick form about your symptoms and medical history. You’ll also want to make sure your internet connection is stable, and your device is charged.
When it’s time, you join the video or phone call. Your doctor asks questions, reviews your symptoms, and may even guide you through a self-exam. It’s a real consultation, just without the waiting room.
After the visit, your doctor might send a prescription to your local pharmacy, share aftercare instructions, or order lab tests if needed. You can usually access everything in your patient portal, making it easy to stay on top of your health from home.
Technologies behind telemedicine
Telemedicine relies on a mix of technologies that work together to make virtual healthcare possible and effective. At the core are telemedicine platforms – specialized software that handles video calls, manages patient records, and allows secure communication between patients and providers.
These platforms are often paired with mobile health apps, which let users book appointments, track symptoms, and stay connected with care teams right from their phones.
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) devices play a big role too. These include tools like blood pressure cuffs, glucose monitors, and wearable fitness trackers that collect health data in real time and send it directly to providers.
Moreover, electronic health records (EHRs) keep everything organized. They store patient information securely and make it easy for doctors to access notes, lab results, or prescriptions during virtual visits.
For communication that doesn’t require a live call, secure messaging tools allow patients to ask questions, upload documents, and receive updates anytime. Of course, all of this depends on reliable connectivity. A stable broadband internet connection, mobile data, or secure Wi-Fi is essential for a smooth telemedicine experience.
The safety of telemedicine
Telemedicine platforms are built with patient safety and privacy in mind. In the U.S., these systems must comply with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), which sets strict standards for protecting health information. Internationally, platforms often follow GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or other regional privacy laws to ensure data is handled securely.
One key layer of protection is end-to-end encryption. This means that video calls, messages, and file transfers are scrambled in a way that only the intended sender and receiver can read them – no one in between can access the information.
To further protect patient data, platforms use authentication and verification steps. Patients may need to log in with two-factor authentication, adding an extra layer of security beyond just a password. On the provider’s side, only verified and licensed professionals can access the platform, ensuring that your medical information stays in the right hands.
Types of Telemedicine
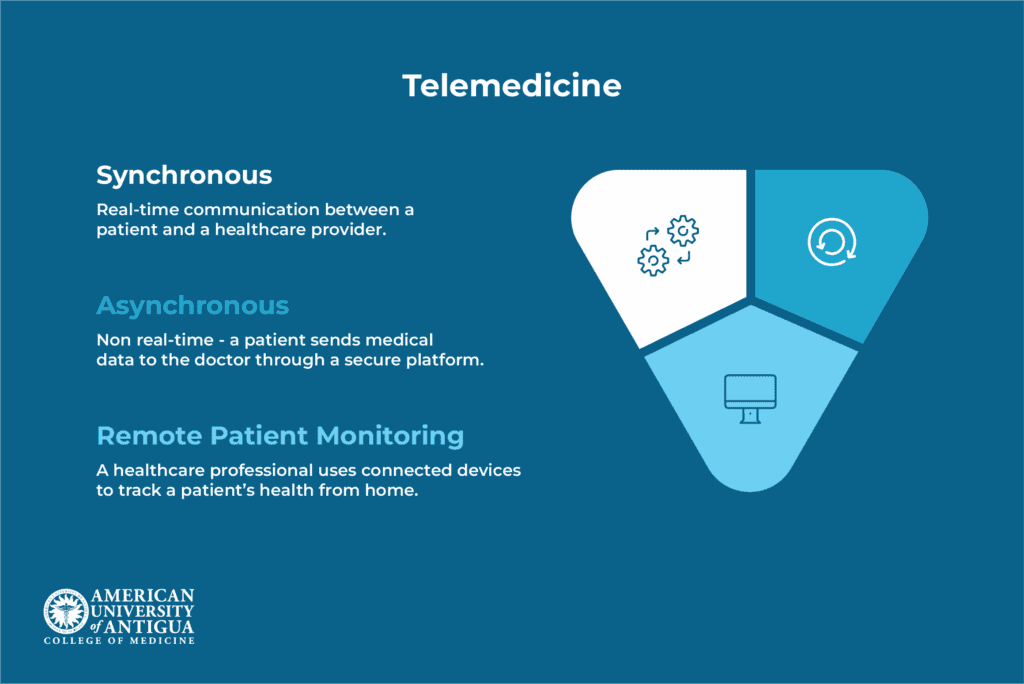
Telemedicine isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It comes in different forms, depending on how and when care is delivered. Some visits happen in real-time through video or phone calls, while others involve sending messages, photos, or health data for review later. However, each type serves unique needs and situations.
Synchronous
Synchronous telemedicine refers to real-time communication between a patient and a healthcare provider. This usually happens through a video call or phone consultation, allowing both parties to talk, ask questions, and make decisions together in the moment.
It’s commonly used for primary care appointments, mental health therapy sessions, and urgent care triage, especially when quick answers or evaluations are needed.
The biggest advantage is the immediacy. Patients can explain their symptoms, get instant feedback, and even ask follow-up questions on the spot. This can lead to faster diagnoses, quicker treatments, and a more personal connection.
However, synchronous telemedicine does come with a few challenges. Appointments still need to be scheduled, so availability can be limited. Plus, live video sessions depend on a good internet connection, and tech issues like lag or dropped calls can interrupt the flow. Still, for many people, it offers a convenient and responsive way to access care.
Asynchronous
Asynchronous telemedicine, also known as “store-and-forward,” involves non-real-time communication between patients and healthcare providers. Instead of meeting live, patients—or referring providers—send medical data such as photos, test results, or health histories through a secure platform. The provider then reviews the information and responds when available, often within a few hours or days.
This method is commonly used in dermatology (for sharing skin images), radiology (to review scans), and tasks like medication refills or progress updates in ongoing treatment plans.
One of the main benefits of asynchronous telemedicine is flexibility. Patients don’t need to schedule a specific time, and it works well even with slower internet or basic tech, making it ideal for rural areas or people with limited digital access. It also uses less bandwidth, which helps reduce connection issues.
However, the lack of live interaction means you can’t ask immediate follow-up questions, and there may be delays in getting a response or diagnosis.
Remote patient monitoring
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is a form of telemedicine that uses connected devices to track a patient’s health from home. These devices, ranging from smartwatches to medical-grade monitors, record vital signs like blood pressure, glucose levels, or oxygen saturation. The data is then automatically sent to a centralized system or provider dashboard, where healthcare teams can review it regularly.
If a reading falls outside the expected range, the system may trigger an alert so providers can respond quickly. This setup helps catch potential issues early, without the patient needing to visit a clinic.
Common use cases include:
- Chronic disease management (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, COPD)
- Post-surgery recovery tracking to monitor healing and prevent complications
- Elder care and fall detection for safer independent living
- Cardiac monitoring after hospital discharge to detect irregularities
RPM supports more personalized and continuous care, especially for those managing long-term conditions or recovering from serious procedures.
Benefits of Telemedicine
Telemedicine offers convenient, accessible, and time-saving healthcare solutions for both patients and providers, making it easier to stay connected and manage health without always needing in-person visits.
For patients
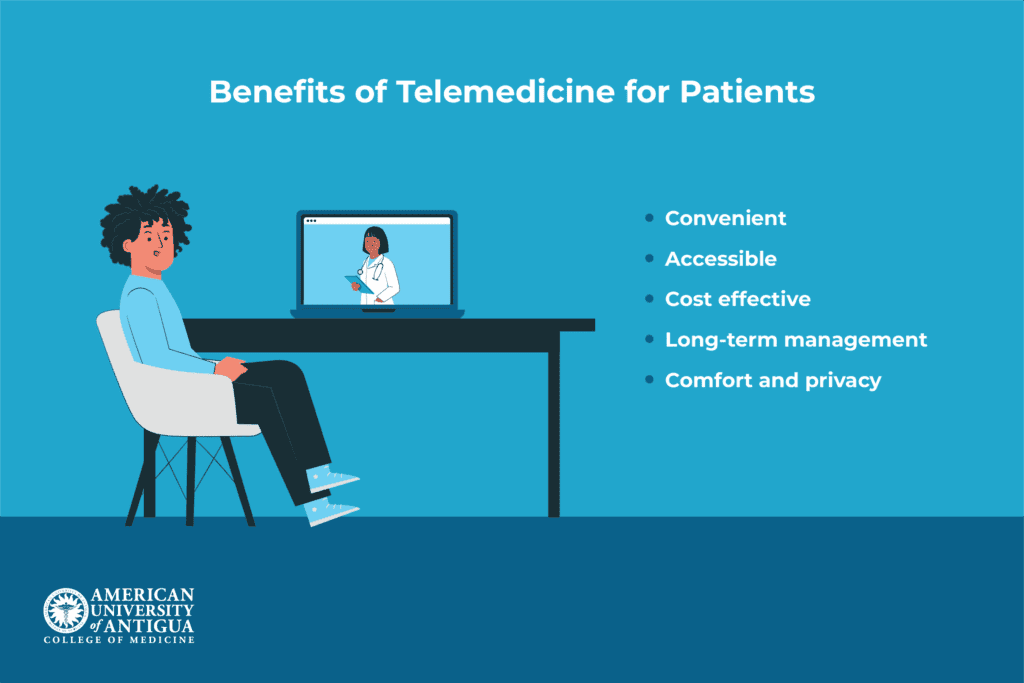
Telemedicine offers several major benefits for patients. First, it provides convenience by eliminating the need for travel, reducing wait times, and making it easier to access care from home.
This is especially valuable for patients in rural or underserved areas where healthcare facilities may be far away. It also leads to cost savings by cutting down on transportation, childcare, and time off work.
Patients with chronic conditions benefit from more frequent follow-ups, leading to better long-term management. Telemedicine also offers improved comfort and privacy, particularly for sensitive issues like mental health or dermatology, allowing patients to discuss concerns in a more comfortable, confidential setting.
All of these factors make telemedicine an appealing and accessible option for many individuals seeking healthcare.
For providers
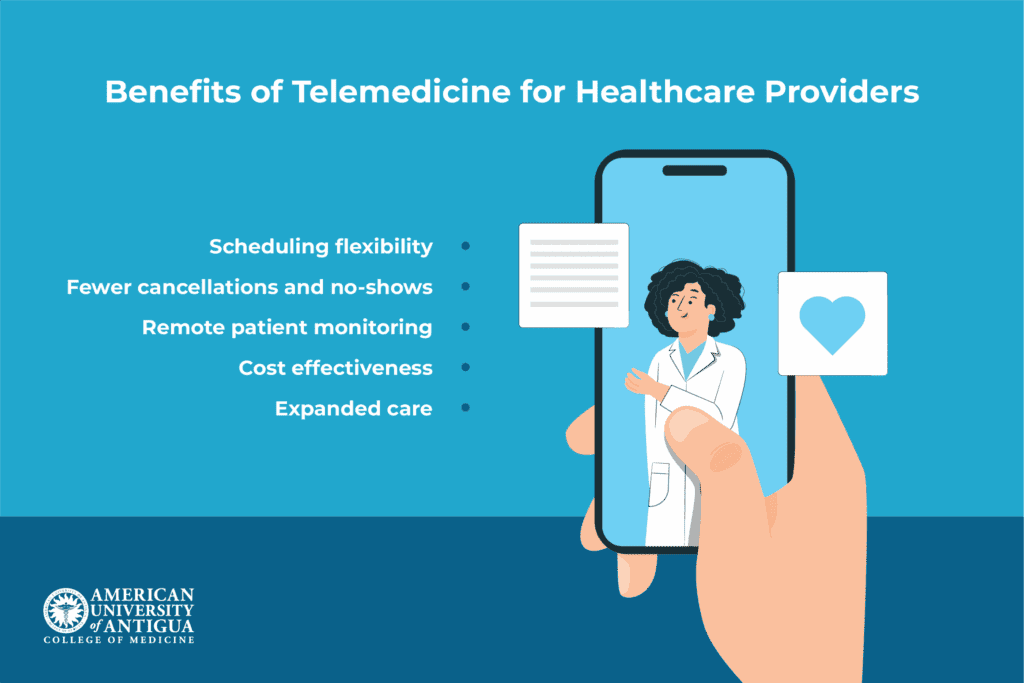
For providers, telemedicine offers increased scheduling flexibility and better management of patient loads, allowing for more efficient use of time. The ease of access also results in fewer no-shows and cancellations, as patients find it easier to attend virtual appointments.
Providers can monitor patients remotely, which allows for earlier intervention if health metrics indicate a problem. This is especially beneficial for chronic care management. Telemedicine also helps reduce overhead costs for certain services, like follow-up visits or consultations, by eliminating the need for physical office space and administrative staff.
Finally, it expands a provider’s reach, allowing them to care for patients beyond their immediate geographic area, increasing accessibility to healthcare.
For healthcare systems
Telemedicine is a game-changer for healthcare systems. It helps ease the pressure on emergency rooms and urgent care by offering patients an easy alternative for non-urgent issues.
This means doctors can focus on more critical cases, and patients can get quicker care. It also makes triaging patients easier, so providers can decide quickly if they need to see someone in person or if a virtual visit will do the job.
What’s great about telemedicine is that it allows healthcare systems to expand care without needing to build more facilities or hire extra staff. It brings healthcare to more people, especially those in rural or underserved areas.
On top of that, telemedicine helps lower costs. When problems are caught early, and chronic conditions are managed remotely, hospital visits and readmissions are reduced, making healthcare more affordable and accessible for everyone.
The Future of Telemedicine
The future of telemedicine is becoming even more exciting with the help of new technologies like AI and machine learning. These tools are already making virtual care smarter. For example, automated triage and symptom checkers use AI to quickly assess a patient’s symptoms and recommend the best course of action.
And then you have predictive analytics that helps doctors manage chronic conditions by spotting early signs of trouble, while intelligent scheduling and patient engagement tools make it easier for patients to book appointments and stay in touch with their providers.
Another big change is the growing use of wearables and IoT health devices. These devices—like smartwatches and fitness trackers—can collect real-time data, such as heart rate or glucose levels, and send it directly to doctors for continuous monitoring.
In more advanced cases, tele-robotics and remote surgery are pushing the boundaries even further. These technologies allow doctors to perform complex procedures from a distance, which is especially helpful in rural areas or places where specialized care is hard to find. As these technologies improve, telemedicine will keep becoming more efficient and accessible for everyone.
Conclusion
Telemedicine is changing the way we think about healthcare, making it faster, more flexible, and easier to access for patients and providers alike. From virtual doctor visits to smart devices tracking your health, it’s clear that digital care is here to stay.
As technology continues to grow, so will the opportunities in this exciting field. If you’re passionate about combining medicine with innovation, join the MD program at AUA and take the first step toward a future in telemedicine. It’s more than just virtual visits—it’s the future of healthcare, and you can be part of it.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What is the difference between telemedicine and traditional care?
Telemedicine lets you see a doctor remotely through video or phone, while traditional care involves in-person visits at a clinic or hospital.
Is telemedicine covered by insurance?
Yes, many insurance plans cover telemedicine, but coverage can vary based on provider and location.
Can telemedicine doctors prescribe medication?
Yes, licensed telemedicine doctors can prescribe medications, including for chronic conditions and minor illnesses, when appropriate.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!