What Is Noninvasive Cardiology? Key Tests & Benefits
Key Takeaways
- Noninvasive cardiology uses simple, painless tests to examine the heart without surgery, helping doctors detect heart problems early.
- Common tests include ECGs, heart ultrasounds, stress tests, heart monitors, and advanced imaging like CT and MRI scans.
- These tests are safe, usually less expensive, and give quicker results compared to surgical procedures.
- Early detection of heart issues allows for more effective treatment and helps prevent serious complications.
Heart health is a growing concern as heart disease affects millions worldwide. Early diagnosis is crucial for ensuring effective treatment and better outcomes. Noninvasive cardiology plays a vital role by using tests and procedures that do not involve surgery or entering the body to assess and monitor the heart. These safe and comfortable methods enable doctors to detect and manage heart conditions early, improving patient care and helping people lead healthier lives.
This article will explore what noninvasive cardiology is, how it compares to invasive cardiology, the common tests used, and the key benefits of these approaches.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!
What Is Noninvasive Cardiology?
Noninvasive cardiology is a type of heart care that evaluates how the heart is working without entering the body or breaking the skin. It uses simple, safe tests like electrocardiograms (EKGs), echocardiograms (heart ultrasounds), stress tests, and heart scans to assess heart health. These procedures are painless and do not require surgery or the use of needles inside the body.
The primary goal of noninvasive cardiology is to find heart problems early, monitor existing conditions, and help doctors choose the best treatment — all without the recovery time and risks associated with more invasive methods.
Noninvasive vs. Invasive Cardiology
Noninvasive and invasive cardiology are two different approaches doctors use to examine and treat the heart. The main difference lies in whether the body is physically entered. Noninvasive cardiology does not involve any cuts, surgical tools, or procedures that go inside the body.
It is mainly used to diagnose potential heart issues through simple, painless tests like EKGs, heart ultrasounds, and stress tests. These help doctors understand how the heart is functioning without any internal procedures.
On the other hand, invasive cardiology involves entering the body. This may include inserting thin tubes called catheters into blood arteries or performing surgical procedures.
Invasive methods are frequently employed to address cardiac problems, such as opening clogged arteries or implanting tiny devices to improve blood flow. In short, noninvasive cardiology helps find the problem, while invasive cardiology focuses on treating them.
Common Noninvasive Cardiology Tests
Doctors often use noninvasive tests to check for heart problems. These tests are used all over the world because they’re generally safe, painless, and do not require going inside the body. They assist healthcare professionals in monitoring heart function and identifying potential problems early.
Holter monitoring, stress testing, echocardiograms, electrocardiograms (ECG or EKG), and imaging techniques are some of the most popular noninvasive cardiac tests. In the following paragraphs, we’ll look at each of these tests in more detail to help you understand how they contribute to maintaining heart health.
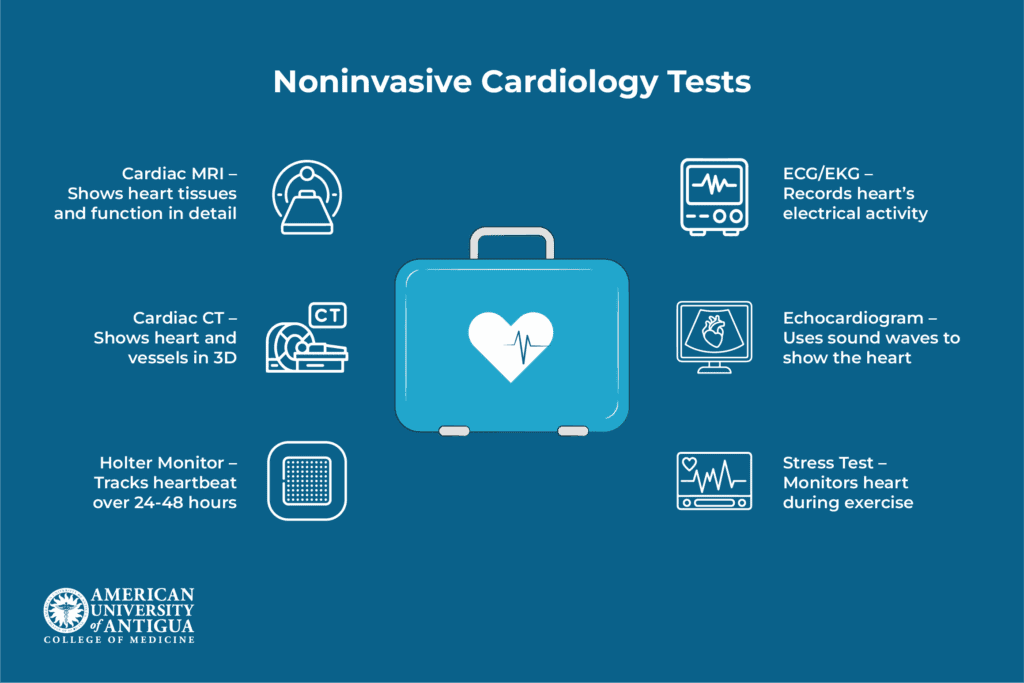
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
An electrocardiogram, also known as an ECG or EKG, is a simple and quick test used to measure the heart’s electrical activity. It shows how fast the heart is beating and whether the rhythm is steady or not.
To perform the test, a doctor or nurse places small adhesive patches called electrodes on the patient’s arms, legs, and chest. These are linked to a device that logs cardiac signals. The test is painless and takes only a few minutes.
An ECG is often the first test physicians order when a patient reports symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath. It can help detect signs of a heart attack, arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), and other heart conditions.
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a common test that creates images of the heart using sound waves. It works similarly to an ultrasound used during pregnancy.
A technician moves over the chest a small device called a transducer. This technology sends sound waves into the body, which bounce off the heart and produce detailed images on a screen.
Doctors use these images to assess the heart’s size, shape, pumping capacity, and how well the valves are functioning. Echocardiograms are frequently performed during routine heart checkups or when a patient reports symptoms like chest pain or difficulty breathing.
Stress testing
Doctors use stress testing to evaluate how the heart performs during physical activity. During the test, you often walk on a treadmill or ride a stationary bike while medical professionals monitor your heart using specialized equipment that tracks your heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs.
This helps doctors determine whether your heart is pumping enough blood and if it maintains a normal rhythm when you’re moving. Stress tests are mostly used to evaluate a patient’s heart health after surgery or a heart attack or when doctors suspect underlying heart disease.
Holter monitoring
Holter monitoring is a test in which you wear a small, portable device that records your heartbeat continuously for 24 to 48 hours. Unlike a standard ECG that captures data over a few minutes, this test monitors your heart’s activity as you go about your daily routine – whether walking, sleeping, or working.
This helps physicians identify cardiac issues that would not be detected during a short clinic visit. Holter monitoring is especially helpful for identifying irregular heartbeats or other intermittent problems that come and go throughout the day or night.
Cardiac CT & MRI
Cardiac CT and MRI are advanced imaging tests that provide clear, detailed pictures of the heart. A cardiac CT scan is especially helpful for examining the heart’s blood vessels and detecting blockages that may be causing discomfort in the chest or other symptoms.
Cardiac MRI is usually used to assess how well the heart is functioning or look for damage following a heart attack since it provides better images of the heart’s soft tissues.
These tests are employed to gather precise information that cannot be obtained from standard tests, such as ECGs or ultrasounds.
Benefits of Noninvasive Cardiology
Noninvasive cardiology offers many valuable benefits for both patients and healthcare providers. It allows the detection and monitoring of heart problems without the need for surgery or instruments entering the body. These tests are usually safer, quicker, and more affordable than invasive procedures.

In the following paragraphs, we’ll take a close look at the key advantages of noninvasive cardiology.
No surgical risk
Noninvasive cardiology tests do not require incisions, anesthesia, or operating rooms. Since nothing goes inside the body, there is no risk of infection, bleeding, or other complications that can occur with surgery.
This makes these tests much safer for everyone, including older adults and those with other health issues. They are also easier and more comfortable for patients. Most people can go back to their normal activities right after the test.
Cost-effective
Noninvasive heart tests usually cost less than invasive procedures because they don’t involve surgery, hospital stays, or lengthy recovery. This helps keep the cost of care lower.
As a result, more people can afford to have their hearts checked, whether for routine checkups or early detection. These tests make heart care more accessible and help prevent serious problems before they start.
Fast diagnosis
Many noninvasive tests, like ECGs and echocardiograms, can be performed quickly, often right in a doctor’s office or clinic. These tests don’t take much time, and the results are usually available the same day or shortly after.
This helps doctors diagnose conditions faster and determine the best treatment sooner. Early detection is very important as it helps prevent heart issues from turning into medical emergencies.
Conclusion
Noninvasive cardiology plays an essential role in diagnosing and monitoring heart conditions safely, quickly, and without the need for surgery. From ECGs and echocardiograms to stress tests and advanced imaging, these methods help doctors detect heart problems early, reduce risks, and improve patient care.
In addition to being effective, noninvasive methods are often more affordable and accessible, making them a valuable tool in preventive heart care.
To learn more about how noninvasive cardiology is shaping the future of cardiovascular medicine, explore the resources and MD program available at AUAMED.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between an interventional cardiologist and an invasive cardiologist?
An interventional cardiologist performs minimally invasive procedures — such as angioplasty or stent placement — to treat heart conditions. An invasive cardiologist is a broader term that refers to any cardiologist who uses catheter-based techniques, whether for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
How long does it take to become a cardiac sonographer or technician?
Training to become a cardiac sonographer or cardiovascular technician typically takes 1 to 2 years, either through a specialized certificate program or an associate degree from an accredited institution
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!