What Is an Endocrinologist and Their Role in Healthcare
Endocrinology, an essential field of medicine, centers on the complex system of glands and hormones that control numerous bodily functions. Endocrinologists, experts in hormone-related health, are necessary for diagnosing and treating conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, and osteoporosis. In an era where lifestyle diseases are on the rise, the relevance of endocrinology in modern medicine has never been more pronounced. Understanding the role of endocrinologists is essential, as their expertise is pivotal in managing and enhancing the health and quality of life of individuals with endocrine disorders.
What Is an Endocrinologist?
Endocrinologists, as medical specialists, are uniquely dedicated to understanding and managing the endocrine system, which encompasses the glands that produce hormones. These hormones regulate numerous bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Endocrinologists diagnose and treat conditions caused by hormonal imbalances, such as diabetes, thyroid diseases, and adrenal disorders.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!
YOUR PATH TO SUCCESS BEGINS HERE
The field of endocrinology is inherently interdisciplinary, integrating aspects of both medicine and biology to provide a comprehensive understanding of how hormones influence health and disease. This unique blend of disciplines allows endocrinologists to offer specialized care that addresses the complex interactions within the endocrine system, making their role in managing hormonal imbalances crucial.
What Does an Endocrinologist Do?
Endocrinologists are specialists who focus on diagnosing and treating hormone imbalances and disorders. Their primary responsibilities include evaluating patients with symptoms of endocrine dysfunction and determining the underlying causes of these issues. They manage chronic conditions such as diabetes by monitoring blood sugar levels and adjusting medications, while also providing education on lifestyle changes.
Endocrinologists assess thyroid function through blood tests and imaging for thyroid disorders, prescribing treatments ranging from hormone replacement therapy to surgical interventions, if necessary. They also address infertility issues by evaluating hormonal influences on reproductive health and offering treatments to enhance fertility. Additionally, endocrinologists use various diagnostic tools, such as blood tests for measuring hormone levels, imaging techniques like ultrasounds and MRIs for visualizing glandular structures, and specialized tests for assessing metabolic functions.
This comprehensive approach, which involves a thorough evaluation and the use of various diagnostic tools, allows them to develop personalized treatment plans to restore hormonal balance and improve patient outcomes.
Common Conditions Treated by Endocrinologists
Endocrinologists treat a wide range of endocrine disorders, with diabetes mellitus being among the most prevalent. Type 1 diabetes involves an autoimmune attack on the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas, necessitating lifelong insulin therapy. Type 2 diabetes, characterized by insulin resistance, often necessitates a combination of medication, dietary changes, and exercise management.
Thyroid disorders are also common. Hypothyroidism results from an underactive thyroid gland, leading to fatigue and weight gain, while hyperthyroidism, caused by an overactive thyroid, can cause symptoms like weight loss and anxiety. Adrenal disorders such as Cushing’s syndrome, marked by excessive cortisol production, and Addison’s disease, characterized by insufficient cortisol production, are also within the purview of endocrinologists.
Other conditions include osteoporosis, which involves weakened bones due to hormonal imbalances, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a reproductive disorder caused by insulin resistance and hormonal dysfunction. Endocrinologists manage these conditions through specialized care to improve patient’s health and quality of life.
Subspecialties Within Endocrinology
Endocrinology encompasses various subspecialties that cater to specific patient demographics and conditions. Pediatric endocrinology focuses on children’s endocrine disorders, such as growth hormone deficiencies, early or delayed puberty, and type 1 diabetes. This subspecialty ensures that young patients receive age-appropriate care and treatment to support their development and overall health. Reproductive endocrinology deals with fertility issues and hormonal imbalances affecting reproductive health in both men and women. Specialists in this field manage conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and male infertility, often employing advanced reproductive technologies and treatments.
Other subspecialties include thyroidology, which focuses exclusively on thyroid disorders, and neuroendocrinology, which studies the interactions between the endocrine and nervous systems. These subspecialties allow endocrinologists to provide targeted and effective care, addressing the unique needs of diverse patient populations and making them feel valued and understood.
How to Become an Endocrinologist
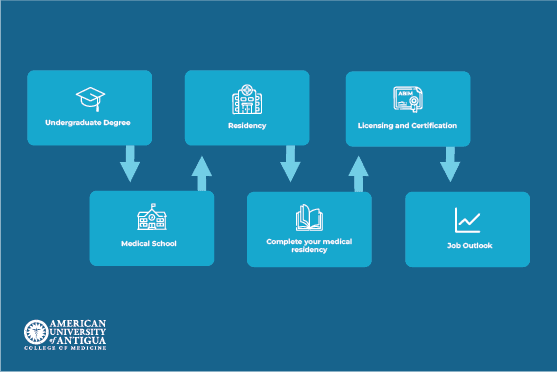
Becoming an endocrinologist involves a rigorous educational and training pathway. Aspiring endocrinologists must first complete an undergraduate degree, typically with a focus on pre-medical courses such as biology, chemistry, and physics. Following this, they must attend medical school to earn a Doctor of Medicine (MD) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree, which usually takes four years. Following medical school, graduates embark on a three-year residency program in internal medicine, during which they acquire extensive clinical experience.
Subsequently, they must complete a fellowship in endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism, which typically takes an additional two to three years of specialized training. To practice as an endocrinologist, individuals must obtain a medical license, which requires passing licensing exams. The positive job outlook and competitive salary range offers aspiring endocrinologists an optimistic view of their future career prospects.
Additionally, board certification in endocrinology is highly recommended and requires passing the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) exam in endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism. This certification is a testament to the rigorous training and expertise of endocrinologists, ensuring they are well-equipped to diagnose and manage complex endocrine disorders. Endocrinology fellowships are competitive, often requiring excellent academic performance, strong letters of recommendation, and relevant research or clinical experience. This comprehensive training, coupled with board certification, ensures endocrinologists are well-prepared to provide high-quality medical care.
Where Do Endocrinologists Work?
Endocrinologists can be found working in various settings, each offering distinct opportunities. Hospitals are common workplaces where endocrinologists provide specialized care for inpatients with complex endocrine disorders and collaborate with other medical professionals. Clinics, including those associated with health systems or independent practices, offer outpatient care for ongoing management of diabetes and thyroid disorders.
Academic institutions are another key environment where endocrinologists teach medical students, as well as conduct research to advance the field. Research settings that may be affiliated with universities or dedicated research organizations allow endocrinologists to investigate new treatments and better understand endocrine disorders. Additionally, private and group practices offer a more personalized approach to patient care, allowing endocrinologists to build long-term relationships with their patients.
Work settings may vary significantly based on subspecialty and individual career goals, with some endocrinologists focusing on clinical practice while others may prioritize research or academic contributions.
Technological Advances in Endocrinology
Technological advancements have greatly revolutionized endocrinology, bringing forth an array of cutting-edge diagnostic tools and treatment options that improve patient care. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and insulin pumps have revolutionized diabetes management by providing real-time glucose data and precise insulin delivery, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing patients’ quality of life.
Telemedicine has also become critical, allowing endocrinologists to monitor patients’ conditions remotely and adjust treatments promptly. Furthermore, genetic testing and molecular diagnostics have opened new avenues for personalized medicine, enabling endocrinologists to identify specific genetic mutations and tailor treatments to individual patients’ needs.
These technological breakthroughs are improving patient outcomes and advancing our understanding of endocrine diseases, paving the way for future innovations and more effective therapies.
Salary and Job Outlook
As of June 27, the average salary for an endocrinologist in the United States is approximately $258,099. Several factors can influence this salary range, including geographic location, years of experience, and the type of practice. Endocrinologists in urban areas or regions with higher living costs often earn more than their counterparts in rural areas. Additionally, those with more years of experience or leadership roles may command higher salaries.
The job outlook for endocrinologists is generally favorable, with overall employment of physicians and surgeons expected to increase by 3% from 2022 to 2032, aligning with the average employment growth rate for all professions. This growth reflects an increasing demand for specialized medical care, driven by an aging population and a rising prevalence of chronic endocrine conditions.
The Importance of Patient Education and Support
Endocrinologists stress the vital importance of patient education and support in managing chronic endocrine disorders, understanding that knowledgeable patients are more likely to follow treatment plans and adopt healthier lifestyles. They provide comprehensive guidance on lifestyle changes, such as balanced diets, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques, which are essential for controlling conditions like diabetes, obesity, and thyroid disorders.
Besides individual counseling, endocrinologists often recommend that patients join support groups, where they get to share experiences, exchange advice, connect with others, and receive emotional support from those dealing with similar issues. Educational workshops and resources are also provided to help patients understand their conditions, the importance of taking medication regularly, and the impact of lifestyle factors on their health.
By equipping patients with knowledge and cultivating a supportive community, endocrinologists enable individuals to actively manage their health, resulting in better long-term outcomes and an enhanced quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, endocrinologists play a crucial role in managing and treating hormone-related disorders such as diabetes, thyroid diseases, and adrenal conditions. Their specialized career path involves extensive medical school, residency, and fellowship training. With a favorable job outlook and competitive salaries, endocrinology offers a rewarding career for those dedicated to advancing patient care and managing complex endocrine health issues.
Begin your journey in the world of endocrinology by exploring the American University of Antigua (AUA) College of Medicine for more information on educational and career opportunities related to the field.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does an endocrinologist differ from a general practitioner?
An endocrinologist specializes in diagnosing and treating hormone-related disorders, while a general practitioner offers general medical care for various health issues.
How long does it take to become an endocrinologist?
Becoming an endocrinologist typically takes about 13-14 years, including undergraduate education, medical school, residency program, and fellowship.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!