How to Become a Diagnostician: Requirements and Career Guide
- Diagnosticians play a vital role in ensuring patients’ well-being by diagnosing and treating medical conditions.
- Becoming a diagnostician requires a bachelor’s degree in a field related to medicine, followed by medical school, residency programs, certifications, and work experience.
- The average annual salary for a diagnostician is around $100,890, with job growth expected to increase by 11% through 2033.
- Key skills that help diagnostics succeed include critical thinking, analytical, interpersonal, and problem-solving.
Did you know that around 8,900 job openings for medical scientists are projected each year? This increasing demand includes diagnosticians – medical professionals who specialize in identifying and diagnosing medical conditions. Becoming a diagnostician offers a rewarding career path for those passionate about healthcare and problem-solving.
Still unsure whether a career in diagnostics is right for you? Keep reading as we introduce you to the requirements of becoming a diagnostician, salary expectations, and job opportunities. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clearer, more informed perspective on whether this career is the right fit for you.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!
YOUR PATH TO SUCCESS BEGINS HERE
What Does a Diagnostician Do?
A diagnostician’s responsibilities can vary depending on the cases they handle — whether they’re complex, rare, or routine. However, their primary role is to identify and diagnose medical conditions in healthcare fields, or, depending on their specialization, evaluate learning or developmental needs in education.
Diagnosticians spend a lot of time with patients to determine the ideal treatment plan. For more challenging cases, they may work longer hours to research and test diagnoses before reaching a final decision. Here are some common tasks and responsibilities of a diagnostician:
- Performing medical tests to identify symptoms or conditions in patients;
- Analyzing patient symptoms and reviewing medical history to diagnose and treat conditions;
- Evaluating and examining test results to recognize potential conditions;
- Designing treatment plans based on the diagnosis, including medication, therapy, or surgery;
- Monitoring and reviewing patients’ progress during treatment.
Steps to Become a Diagnostician
As diagnosticians are significant to the medical field, they need to follow specific requirements to successfully pursue a career in this field. Their journey begins with earning a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field, then moves on to medical school, residency, and obtaining any necessary certifications. Lastly, they need to gain hands-on experience and refine their skills.
Here’s a more detailed description of the steps you can take to become a diagnostician.
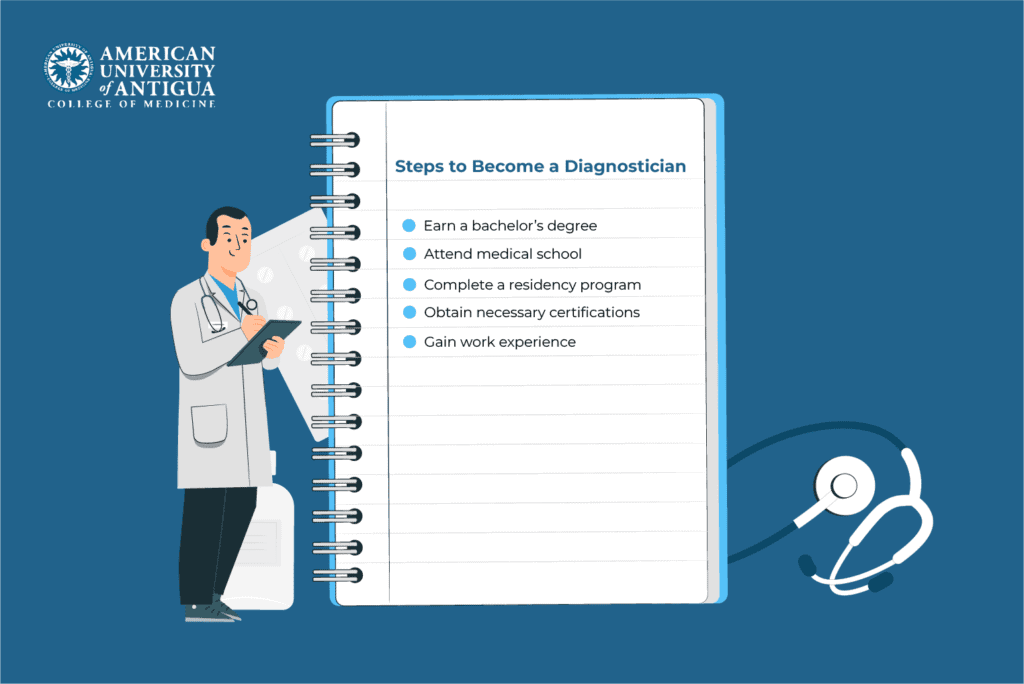
Earn a bachelor’s degree
The first step towards becoming a diagnostician is earning a 4-year bachelor’s degree from an accredited college or university. You’ll want to major in subjects related to medicine, such as health science, biology, chemistry, or pre-medicine.
These courses will lay a strong foundation for your future career as a diagnostician. For instance, subjects like anatomy, physiology, epidemiology, biochemistry, medical ethics, and global health will not only prepare you for medical school but also give you a deeper understanding of the human body and healthcare systems.
Attend medical school
After completing your bachelor’s degree, you can continue pursuing a medical degree. Diagnosticians are required to attend medical school to gain the necessary knowledge and skills required to practice in the field, making this an essential part of your journey.
Medical school typically lasts 4 years. The first 2 years focus on classroom and laboratory learning, where you will explore subjects such as anatomy, physiology, pathology, and diagnostics. During the last 2 years, you’ll participate in clinical rotations where you’ll work alongside residents in various specialties like surgery, pediatrics, internal medicine, or psychiatry.
Before applying to medical school, you should inquire about any specific entry requirements, such as a Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) score, and consider other relevant factors to ensure you’re prepared for the application process and choose the right school.
Complete a residency program
A residency program is a crucial step in advancing your medical education and training after medical school. During this period, residents gain hands-on experience in diagnosing various conditions and mastering diagnostic techniques. They work under the supervision of experienced physicians and medical staff in hospitals or other healthcare settings, developing practical, real-world training.
This demanding period requires residents to work long hours in order to gain the skills, knowledge, and expertise needed to become a diagnostician. Residency programs typically last 3 to 7 years, depending on the specialty. To become a diagnostician, you may choose to pursue a 4-year residency in diagnostic radiation, a 3-year program in internal medicine, or a 4-year program in pathology or clinical pathology.
Obtain necessary certifications
Certification is highly important for a diagnostician to set themselves apart as experts in the field and demonstrate their commitment to patient care. Once education and training are complete, they must pass a board certification exam that tests their knowledge in specific medical fields, such as internal medicine, pathology, or another relevant specialty. This certification can be required by the state or national medical boards, emphasizing its importance even further.
There are multiple paths to becoming a diagnostician, depending on your field of specialization. For example, you can pursue certification in pathology, radiology, internal medicine, or clinical pathology. These certifications are granted by professional associations such as the American Board of Pathology (ABP), the American Board of Radiology (ABR), or the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM).
Additionally, diagnosticians can opt for specialty certifications, including Medical Laboratory Scientist (MLS), Clinical Laboratory Scientist (CLS), or Specialist in Blood Banking (SBB). These certifications are essential for building a rapport with patients and earning their trust, demonstrating professional accomplishment, and opening doors to higher-paying job positions.
Gain work experience
Although it is essential to possess extensive medical knowledge and specialization, graduates are required to apply their skills to practice. The last step on your journey to officially becoming a diagnostician is gaining hands-on work experience in clinical or healthcare settings.
You can gain experience by assisting healthcare professionals, participating in medical internships or externships, and volunteering. These opportunities enable you to build confidence and expertise in diagnosing conditions, performing tests, and developing treatment plans — all core responsibilities of a diagnostician.
Essential Skills for Diagnosticians
Apart from education, training, residency, certification, and work experience, diagnosticians are required to possess certain skills that help them succeed in this field, including:
- Analytical skills: Diagnosticians often handle complex cases, where the ability to effectively analyze data from tests and research is essential for reaching evidence-based conclusions and solving diagnostic challenges;
- Attention to detail: Strong attention to detail allows diagnosticians to identify subtle symptoms and medical conditions, enabling them to reach diagnoses quickly and accurately;
- Problem-solving skills: Crucial for delivering high-quality patient care, problem-solving skills are also important for tackling potential challenges that may arise during the diagnosis or treatment process;
- Interpersonal skills: Considering that diagnosticians frequently interact with patients and collaborate with medical staff, effective interpersonal skills are essential for building trust, communicating clearly, and fostering teamwork.

Salary and Job Outlook
The average salary for diagnosticians ranges from $193,149 to $254,180 per year, though this can vary depending on the specialty, location, and experience. For example, diagnostic radiologists who are in higher demand, earn an average salary of $467,383 annually. Additionally, larger cities such as San Jose offer higher salaries for diagnosticians, with an average of $284,730 per year.
Employment for medical scientists, including diagnosticians, is expected to grow by 11% through 2033, which is faster than the average for other medical professions. By 2033, approximately 163,400 diagnosticians are expected to be employed. This growth is driven by medical technology innovations, a growing need for personalized medicine, and an increased focus on preventative care.
Additionally, the demand for diagnosticians is further fueled by an aging population and a global spread of diseases. This demonstrates the need for medical research in various conditions, such as Alzheimer’s, cancer, and antibiotic resistance. Such factors enable diagnosticians to hold an important position in healthcare and address some of the industry’s biggest challenges.
Is a Career as a Diagnostician Right for You?
When considering whether a career as a diagnostician is right for you, reflect on your personal interests, skills, and career goals. The role of a diagnostician includes solving complex problems and working with diverse data to reach decisions and design treatment plans.
They also need to demonstrate curiosity, perseverance, and strong communication skills. Although the path to becoming a diagnostician can be extensive, this role can be greatly satisfying for those who enjoy critical thinking and analytical challenges. If these qualities resonate with you, a career as a diagnostician could be an ideal choice for you.
Conclusion
Diagnosticians play a significant role in the medical industry and the overall well-being of patients. Their primary role is identifying, diagnosing, treating, and preventing complex medical conditions. The path to becoming a diagnostician includes pursuing education, residency, certification, and work experience. It is a highly rewarding career in terms of both financial and job stability, especially for those who become board-certified.
If you’re interested in working with patients, analyzing symptoms, and have strong interpersonal skills, this could be the perfect career for you. Start building your future today by exploring our medical school program at the American University of Antigua College of Medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to become a diagnostician?
It typically takes around 12 years to become a diagnostician. This includes a 4-year pre-medical bachelor’s degree, followed by 4 years of medical school, and then 3 to 4 years of residency, certifications, along with certifications and work experience.
What is the difference between a diagnostician and a doctor?
Technically, all diagnosticians are doctors. However, a diagnostician specializes in identifying and diagnosing medical cases, often complex or rare. On the other hand, “doctor” is a broader term that refers to medical professionals who diagnose, treat, and prevent conditions or illnesses across various specialties.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!