How to Become a Cardiothoracic Surgeon? Revealing Key Steps
Key Takeaways
- Becoming a cardiothoracic surgeon requires years of study, including a bachelor’s degree, medical school, and specialized residency.
- Areas like congenital heart surgery or thoracic surgery offer focused expertise within the field.
- The field offers job security, competitive salaries, and the chance to make a lasting impact on patients’ lives.
Have you ever wondered how to become a cardiothoracic surgeon, the specialist who saves lives through heart and lung surgery? This path is not for the faint of heart—it requires years of intense study, hands-on experience, and unwavering dedication.
From obtaining a bachelor’s degree to completing a residency and fellowship, each phase of this journey sharpens skills and builds expertise. As technology and medical practices evolve, so do the opportunities for those ready to tackle the challenges of this high-demand field.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!
YOUR PATH TO SUCCESS BEGINS HERE
Eager to begin the adventure? Let’s uncover the key steps to becoming a cardiothoracic surgeon.
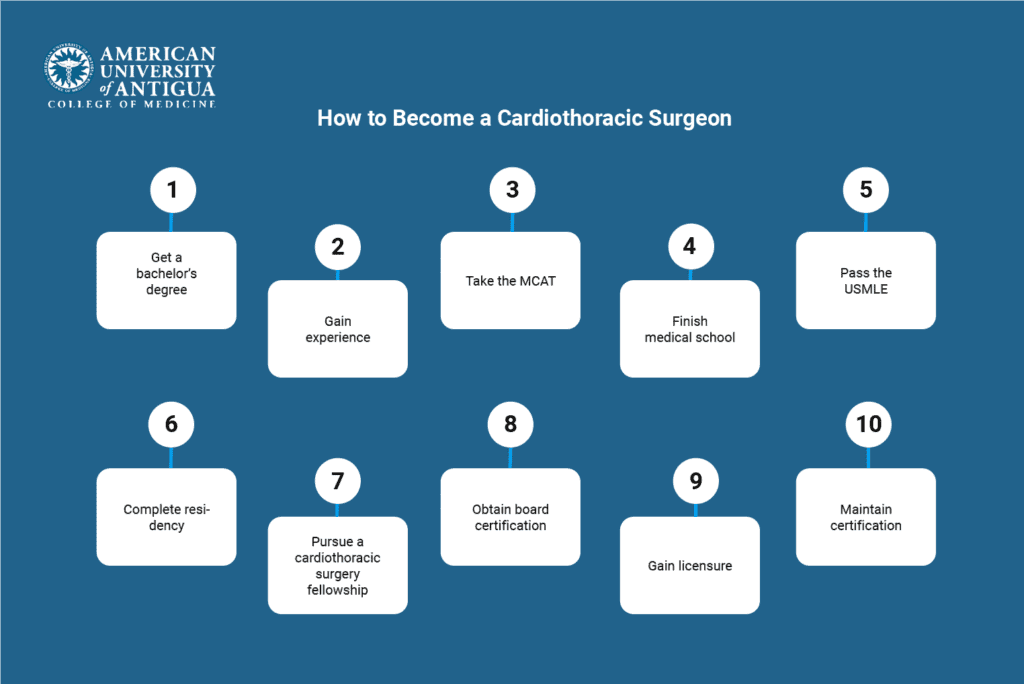
How to Become a Cardiothoracic Surgeon
Cardiothoracic surgeons specialize in diagnosing and treating conditions of the heart, lungs, esophagus, and chest. They perform complex surgeries like heart transplants, bypasses, and lung resections.
Becoming a cardiothoracic surgeon requires dedication, with around 15 years of education and training, including medical school, a general surgery residency, and specialized cardiothoracic training. This path demands skill, precision, and a commitment to saving lives.
1. Get a bachelor’s degree
A bachelor’s degree is a crucial foundation for aspiring cardiothoracic surgeons, as it prepares students for medical school’s academic and practical demands.
Most programs require students to complete coursework in biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics, to meet medical school prerequisites. Having strong performance in these areas demonstrates a candidate’s academic capability and commitment to medicine.
Through a bachelor’s degree, students develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and research skills essential for advanced medical training. Many programs also offer opportunities for laboratory work, internships, and healthcare-related volunteering, providing hands-on experience in medical environments.
This degree not only fulfills academic requirements but also allows students to explore related disciplines, helping them confirm their career interests. Moreover, achieving a strong GPA and excelling in coursework enhances students’ chances of gaining admission to competitive medical schools, a key step toward becoming a cardiothoracic surgeon.
2. Gain experience
Before becoming a cardiothoracic surgeon, gaining clinical experience is pivotal. Picture this: you’re shadowing a surgeon in the operating room, watching life-changing procedures unfold. Experiences like these provide valuable insight into what it takes to handle pressure, precision, and patient care all at once.
You can start by volunteering at a hospital, working as a medical assistant, or joining a research project. Even jobs unrelated to surgery, like helping in a clinic or assisting in labs, teach you valuable lessons about teamwork and problem-solving.
Every hour spent observing and participating sharpens your understanding of what being a surgeon means. By stepping into healthcare early, you’re not just preparing for medical school—you’re proving to yourself that this challenging, rewarding path is one you’re ready to conquer.
3. Take the MCAT
The MCAT, or Medical College Admission Test, is a standardized exam that’s a key step for aspiring doctors. It evaluates critical thinking, problem-solving, and scientific knowledge across four sections: biological sciences, chemical and physical sciences, psychological and social sciences, and critical analysis and reasoning. Scoring well on the MCAT is essential, as medical schools use it as a major admissions criterion.
Passing the MCAT demonstrates your readiness for the academic challenges of medical school, proving you are capable of applying knowledge in practice under pressure, much like what you’ll do as a doctor.
Before taking the test, however, knowing how to study for the MCAT is key. Focus on mastering foundational subjects like biology, chemistry, and physics while also practicing time management and test-taking strategies. You should also familiarize yourself with the exam format through practice tests. A structured study plan and consistent effort will help you build confidence and achieve competitive scores.
4. Finish medical school
Finishing medical school is a pivotal step in becoming a cardiothoracic surgeon. It’s where aspiring doctors deepen their understanding of the human body and learn to diagnose and treat diseases. Over four years, students in medical school learn through a mix of classroom and hands-on experience that shapes them into capable, compassionate healthcare providers.
The first two years focus on foundational sciences like anatomy, pharmacology, and pathology paired with problem-solving in clinical contexts. The latter half brings students into hospitals and clinics, rotating through specialties such as surgery, internal medicine, and pediatrics. These experiences help students build clinical skills and patient interaction confidence.
Graduating from medical school earns students a Doctor of Medicine (MD) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree, opening the door to residency training. Through medical school, future surgeons get equipped with the expertise and real-world exposure needed to thrive in the demanding yet rewarding field of healthcare.
5. Pass the USMLE
Now onto another vital step: passing the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE). This three-step exam evaluates a doctor’s ability to apply medical knowledge in real-world scenarios, ensuring they are ready to provide safe and effective patient care. Successfully completing the USMLE is required to obtain a medical license, which is essential to starting a residency in cardiothoracic surgery.
The USMLE is divided into three steps:
- Step 1 assesses foundational science knowledge.
- Step 2 focuses on clinical skills and patient management.
- Step 3 evaluates the ability to practice medicine independently.
Each step demands thorough preparation and passing scores that vary slightly depending on state requirements.
Students who pass the USMLE demonstrate that they are prepared to progress in their medical education and fulfill the requirements for a license to practice surgery anywhere in the United States, opening the door to a lucrative surgical career.
6. Complete residency
Completing a residency is a key prerequisite to becoming a cardiothoracic surgeon, providing in-depth, hands-on training. Aspiring surgeons typically complete a general surgery residency, which lasts about five years, before pursuing specialized training in cardiothoracic surgery.
Residency immerses doctors in surgical procedures, patient care, and emergency management. They gain skills in diagnosing complex conditions, performing surgeries, and working in high-pressure environments. Residents also learn teamwork and leadership as they collaborate with other healthcare professionals to provide optimal care.
After finishing residency, doctors can pursue fellowships to further specialize or begin practicing as general surgeons. Getting into residency prepares doctors for the demanding, rewarding challenges of a career in cardiothoracic surgery.
7. Pursue a cardiothoracic surgery fellowship
A cardiothoracic surgery fellowship is essential for aspiring surgeons to gain advanced expertise in treating complex conditions of the heart, lungs, and chest. This specialized program, lasting two to three years, provides in-depth training in procedures like heart transplants, coronary artery bypass grafting, and lung resections, as well as minimally invasive and robotic surgeries.
Fellow doctors refine technical precision, decision-making, and patient management skills under the guidance of experienced mentors. They also learn to handle high-pressure situations and collaborate effectively within surgical teams.
Completing this fellowship opens doors to opportunities in top hospitals and academic institutions. Surgeons emerge not only as specialists but also as leaders in their field, prepared to take on challenging cases and contribute to advancements in cardiothoracic medicine.
8. Obtain board certification
After completing a cardiothoracic surgery fellowship, the next step is board certification. This process, governed by the American Board of Thoracic Surgery (ABTS), confirms a surgeon’s expertise and readiness to practice independently. To become board-certified, fellows must pass a comprehensive written and oral examination, demonstrating their proficiency in heart and lung surgeries.
Achieving board certification opens up numerous career opportunities, such as higher-level positions in prestigious hospitals, academic institutions, or private practice. It enhances credibility and assures patients that the surgeon has met the highest standards of care.
Certified surgeons are also more likely to gain privileges for complex procedures and may have access to leadership roles or teaching opportunities in surgical education.
Board certification is a mark of excellence in the field, ensuring cardiothoracic surgeons are fully prepared to provide top-tier care and contribute to the advancement of the specialty.
9. Gain licensure
To gain licensure, aspiring cardiothoracic surgeons must pass the necessary exams, including the USMLE, and meet state-specific requirements. Once licensed, they are authorized to practice medicine and perform surgeries in their state, allowing them to start their careers.
After obtaining licensure, surgeons can continue to advance their education by attending medical conferences, engaging in research, or pursuing additional certifications in specialized areas, such as heart failure or pediatric cardiothoracic surgery.
Career advancement often involves leadership roles in hospitals, teaching positions, or becoming experts in innovative surgical techniques. Surgeons can also choose to focus on specific patient populations, such as transplant surgery or thoracic oncology, further honing their skills.
Continuous learning and professional development allow surgeons to stay at the forefront of medical advancements and provide the best care possible to their patients.
10. Maintain certification
Cardiothoracic surgery is evolving fast, with new technologies, techniques, and research changing the way surgeons approach patient care. To keep up, cardiothoracic surgeons need to stay curious and adaptable.
Regularly attending medical conferences, subscribing to leading journals, and joining professional organizations like the American College of Surgeons are essential. Networking with peers and experts also opens doors to fresh insights and collaborative learning.
Engaging in hands-on training with the latest surgical tools—like robotic surgery systems or minimally invasive techniques—ensures surgeons stay sharp. Surgeons should also embrace lifelong learning, taking advanced courses or fellowships to refine their skills.
Staying updated makes you part of a community that shares innovations and continually pushes the boundaries of what’s possible in heart and lung surgery.
Cardiothoracic Surgeon Responsibilities
Cardiothoracic surgeons are experts in treating conditions of the heart and lungs, including:
- Aortic issues, such as aneurysms or dissections of the aorta
- Heart failure, which entails chronic heart function decline
- Chest injuries, including trauma or damage to the chest organs
- Lung disease, such as lung cancer or emphysema
To manage these conditions effectively, these surgeons take care of patients throughout their entire healing journey.
Before surgery, they:
- Evaluate patient health through tests and imaging
- Discuss the surgical procedure and risks with the patient
- Plan the surgery based on the diagnosis and patient condition
During surgery, they:
- Perform surgeries like heart bypass, valve replacement, or lung resection
- Monitor patient vitals and adjust procedures as needed
After surgery, they:
- Oversee recovery and monitor for complications
- Provide follow-up care and rehabilitation recommendations
Cardiothoracic Surgery Subspecialties
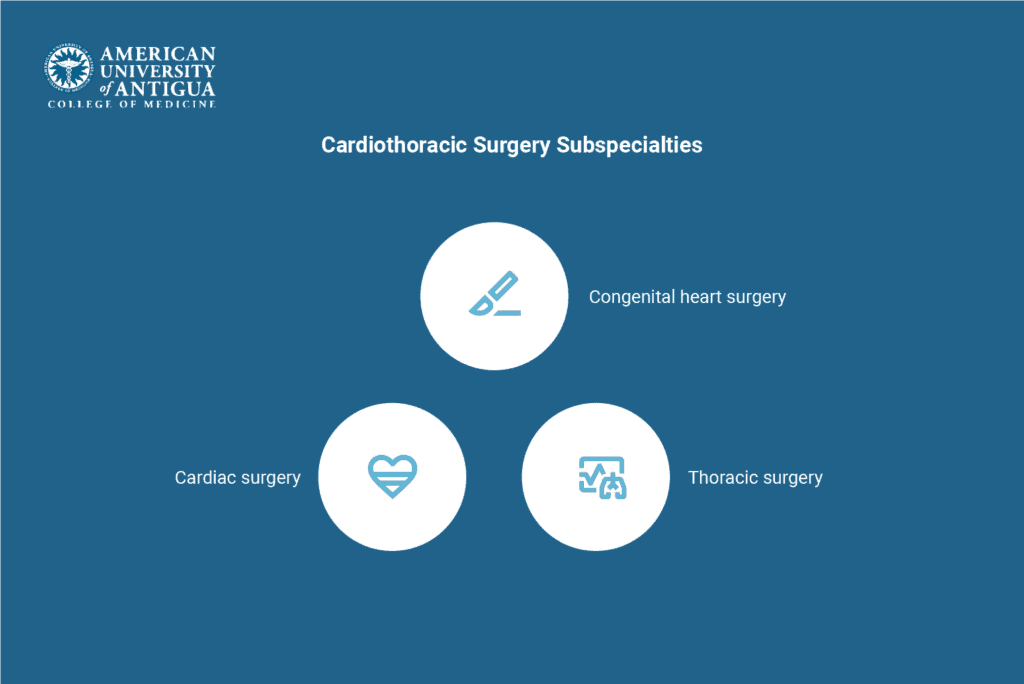
Subspecialties are focused areas of expertise within a broader field of medicine, allowing doctors to concentrate on specific types of conditions or patient groups. In cardiothoracic surgery, subspecialties include:
- Congenital heart surgery, which focuses on surgical treatments for heart defects present at birth.
- Cardiac surgery, which deals with conditions like coronary artery disease, valve issues, and heart failure in adults.
- Thoracic surgery, which specializes in lung, esophagus, and chest conditions, such as lung cancer or chest trauma.
Choosing one of the subspecialties depends on a surgeon’s preferences and career prospects.
Career and Salary Outlook
The demand for cardiothoracic surgeons has steadily increased due to an aging population and rising rates of heart disease and lung conditions. As the baby boomer generation ages, the need for specialized heart and lung care continues to grow, driving demand for these surgeons.
Historically, cardiothoracic surgeons have enjoyed a high salary range, reflecting their extensive training and expertise. Over time, salaries have remained competitive but may slightly adjust due to healthcare reforms and technological advancements. As of now, their annual salary stands at an average of $260,148.
In the future, as the demand for specialized surgeries grows, salaries are likely to remain strong, with potential increases in high-demand areas like cardiac transplant surgery and robotic-assisted procedures.
Conclusion
Becoming a cardiothoracic surgeon is a challenging yet rewarding journey. It requires dedication, beginning with a bachelor’s degree, passing the MCAT, completing medical school, and gaining experience through a residency and fellowship. These surgeons treat a variety of conditions, from heart failure to lung diseases, and specialize in areas like adult cardiac or thoracic surgery, making them critical in healthcare.
Students interested in pursuing this path should explore AUAMED for top-tier education and career opportunities. Your future career in cardiothoracic surgery starts with us!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What is the highest-paid cardiothoracic surgeon?
The highest-paid cardiothoracic surgeons are often those who specialize in complex procedures such as heart transplants or work at prestigious medical institutions.
How competitive is cardiothoracic surgery?
Cardiothoracic surgery is highly competitive, with rigorous requirements for education, training, and experience. The limited number of fellowship positions and the intensity of the specialty make it a challenging field to enter.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!